Decoding Forex Market Volatility
 Decoding Market Volatility
Decoding Market Volatility
Basically, volatility is considered as bad news by most investors as stock market volatility and financial crisis go hand-in-hand. Actually, volatility can sometimes be good news and some other times bad news. In any case, understanding volatility is a key process towards optimizing your portfolio management and maximizing your returns in the long-run.
Volatility can be used either for detecting potential breakouts or for categorizing financial assets based on the level of their risk.
What is Actually Volatility?
Volatility is a statistical tool that measures the degree of variation of a price series by using a standard deviation of returns.
Simple truths about volatility in finance
→ Volatility describes the level of changes in the price of a financial instrument over time
→ Volatility does not imply direction, only risk
→ The more volatile an asset the higher the risk of holding it
→ Measuring volatility is essential in categorizing financial assets based on their risk profile (portfolio management)
→ Volatility may help traders confirming breakout signals (technical analysis)
→ The implied volatility of a financial asset can create seasonality patterns over the years
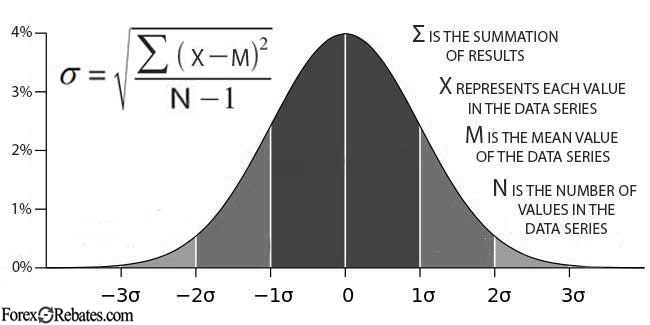
What is a Standard Deviation of Returns?
As it was mentioned before, measuring volatility involves the use of a standard deviation of returns. The standard deviation (SD, or the Greek letter sigma σ) measures the number of variations or dispersions of a set of data values over time. A low SD of returns indicates that the returns of a financial asset tend to be close to the mean number, while a high SD indicates that the returns of a financial asset are spread out over a wide range of values.
Chart: The standard deviation formula
Forex Market Volatility
Forex Market Volatility refers to the amount of risk involved with the fluctuations of a Forex exchange rate. In general, the higher the implied volatility, the riskier the Forex exchange rate.
Explaining Forex Volatility
The Forex market volatility measures the level of changes in the price of a currency pair over time. It doesn’t imply direction.
A higher volatility means that the price of a currency rate can change considerably over a short time period in either direction. A lower volatility means that the price of a currency rate will not fluctuate dramatically over a short time period.
As you can see in the table, the most volatile session is the European session, especially as it ends and overlaps with the New York session. The less volatile session is the Asian session. As an exemption, there are a few pairs with increased volatility during the Asian session, and that includes USDJPY, AUDJPY, and NZDJPY.
The table below shows the volatility figures of 5 major Forex pairs during the three Forex sessions. Volatility calculations are made using open to close ranges.
Table: Volatility based on 5 Years of Data
|
Currency Pair |
European Session Standard Deviation (%) |
US Session Standard Deviation (%) |
Asian Session Standard Deviation (%) |
|
EURUSD |
0.5473 |
0.4968 |
0.2770 |
|
USDJPY |
0.5292 |
0.5182 |
0.7631 |
|
GBPUSD |
0.5825 |
0.4842 |
0.1899 |
|
USDCHF |
0.5761 |
0.5293 |
0.2701 |
|
EURGBP |
0.5133 |
0.3609 |
0.1796 |
|
Source: TradeStation |
|||
Forex volatility peaks during the three Forex overlaps (European, American, and Asian session overlaps). The overlap between the London and the New York sessions provides the greatest volatility to trade Forex. This is because liquidity peaks as the two markets are opened together and usually when liquidity peaks, volatility peaks as well.
The chart below presents the volatility of all key Forex pairs based on the standard deviations of hourly ranges – highs to lows.
Chart: 24-Hour Volatility Map

The above volatility map refers to the three Forex sessions based on the EST time (US Eastern time). The data covers an average 24-hour period over a 5-year period (Source: TradeStation).
How to Measure Market Volatility?
There are many tools and methods in order to measure market volatility. These are the most important of those tools and methods:
-
Bollinger Bands
The Bollinger Bands is a very popular technical analysis tool invented by John Bollinger in the 1980s. The tool consists of 2 lines and one moving average (MA) in the middle. Each line represents a standard deviation (SD was explained earlier in this article).
Formulating Bollinger Bands
- Moving Average {standard settings: 20-day simple moving average (SMA)}
- Upper Band {standard settings: 20-day SMA + (20-day standard deviation of price x 2)}
- Lower Band {standard settings: 20-day SMA - (20-day standard deviation of price x 2)}
One line is plotted above the moving average and the other is plotted below the moving average. The Bollinger bands are automatically widening when the market volatility increases and narrowing when volatility decreases.
The standard settings can be adjusted to adapt to any new market conditions. But as Mr. Bollinger recommended, make only a small incremental to the standard deviation multiplier. Mr. Bollinger suggested:
-For a 50-period SMA (instead of a 20-period SMA), an increase of the standard deviation multiplier to 2.1 (instead of 2.0)
-For a 10-period SMA, decrease the standard deviation multiplier to 1.9
How you can trade based on the Bollinger Bands -Trading Tips
→ Bollinger Bands can provide an instant definition of high and low. Prices are considered high at the upper Bollinger band and prices are considered low at the lower Bollinger band. This is a very useful feature for recognizing patterns, or for determining trends (higher high / lower low).
→ Some intraday traders buy the market when the price touches the lower band and exit their position when the price touches the moving average in the middle. Also, they sell the market when the price touches the upper band and exit their position when the price touches the moving average in the middle.
→ Some breakout traders buy when the price of an asset breaks above the upper band or sell when the price breaks below the lower band.
→ The Bollinger Bands can be used for generating instantly a key stop-loss level, and that is very useful for day-trading.
→ Volatility option traders apply another strategy based on Bollinger Bands. When the two bands get historically wider, they sell options. When the bands have historically close together, they buy options. This strategy will profit when market volatility returns to the average historical volatility level.
Chart: The Bollinger Bands and ATR on MT4
-
Average True Range (ATR)
The Average True Range (ATR) was introduced by J. Welles Wilder (along with ADX, RSI, and Parabolic SAR). The tool measures the True Range of a price series over a period of time. ATR is based on 14 periods and can be used for measuring volatility in several timeframes (intraday, daily, weekly, or monthly).
ATR uses absolute values to calculate volatility, no matter if the values are positive or negative or not. The True Range is calculated as the greater of:
-
Current period High – Current period low
-
Current period High – Previous period close
-
Current period Low – Previous period close
Using ATR to Trade -Trading Tips
→ Strong swings are usually accompanied by large ATR ranges. This is very helpful at the beginning of a price movement. ATR can confirm the strength of a breakout and help traders to enter in large movements at their early stages.
→ A bullish or bearish reversal accompanied by a significant increase in ATR usually indicates a strong trend reversal.
→ A bullish or bearish resistance/support break accompanied by a significant increase in ATR reinforces the resistance/support break. On the contrary, low ATR indications usually is a sign of a false breakout.
-
Keltner Channels
The Keltner Channels were originally introduced by Chester Keltner in his 1960 book “How to Make Money in Commodities”. The tool was optimized in 1980 by Linda Bradford.
Keltner Channels is a similar tool to Bollinger Bands, as both tools use two volatility-based envelopes and a moving average in the middle.
The Keltner Channels use two Average True Range values above and below a 20-day EMA.
Calculating the Keltner Channels
■ Middle Line: 20-day EMA (exponential moving average)
■ Upper Band: Middle Line + { 2 x ATR (10) }
■ Lower Band: Middle Line – { 2 x ATR (10) }
These are the main differences between the two technical analysis tools:
-
Keltner Channels use two Average True Range (ATR) bands instead of two Standard Deviation (SD)
-
As the ATR generate smoother readings than the SD, the Keltner Channels are less volatile than the Bollinger Bands
-
Keltner Channels use an exponential moving average (20-day EMA) in the middle instead of a simple moving average (20-day SMA)
-
As the exponential moving average (EMA) is more sensitive to recent data than the simple moving average (SMA), the Keltner Channels are more sensitive to real price action than the Bollinger Bands
How you can trade using the Keltner Channels
Keltner Channels can be used for several different tasks:
-
Identify and evaluate the market volatility
-
Identify trend reversal (channel breakouts) and trend continuation
-
Identify strong market movements at its early stages (a strong trend usually start as the price moves above or below the Keltner channel lines)
-
When the price touches the Keltner Channels in close-ranging markets, it is a sign of an overbought or oversold market
Although Keltner Channels is a more sophisticated tool than the Bollinger Bands, more professional Forex traders prefer to use the Bollinger Bands. This is because the Bollinger Bands can better evaluate the market volatility.
-
The Beta (Measuring Stocks Volatility)
Beta is a very popular stock trading tool for measuring the relative volatility of a particular stock compared to the general market. Beta is also referred to as the beta coefficient and it is symbolized by the Greek letter β. Beta is used in the CAPM (capital asset pricing model) in order to forecast the expected return of a basket of stocks based on the expected general market returns.
What is Regression in Finance?
Regression is a statistical tool used to measure the strength of a relationship between certain variables:
-one dependent variable (Y)
-and a series of independent changing variables
Beta Calculation
The Beta calculation is based on historical data. The historical returns of an asset are calculated against the overall market returns for the same period. This can be done in Excel by using a regression formula, as follows:
■ =COVARIANCE.P(asset price, index price)/VAR.P(index price)
The asset prices and index prices cover certain data series, for example:
■ =COVARIANCE.P(A1:A999,B1:B999)/VAR.P(B1:B999)
Alternatively, the slope function can offer the same results:
■ =SLOPE(A1:A999,B1:B999)
What beta readings can indicate for the market?
The beta coefficient can calculate the overall volatility of an asset price against the returns of a relevant index.
-If beta equals 1 (or close), it indicates that the price of an asset moves perfectly in line with the index used as a benchmark
-If beta is considerably less than 1, it indicates that the asset is less volatile than the index used as a benchmark market
-If beta is considerably more than 1, it indicates that the asset is more volatile than the index used as a benchmark market
How to Trade based on Beta -Trading Tips
As it was mentioned before, the beta can indicate whether an asset is more or less volatile than the overall market. That information can be very useful when trading stocks.
→ When you anticipate the overall market is going up you buy stocks with very high beta (β>1.45)
→ When you anticipate the overall market is going down you sell stocks with very high beta (β>1.45)
→ When you are not sure about where the market is going you diversify your portfolio by adding stocks with a different beta coefficient. That means if you buy 2 stocks with β>1.25, you buy also two stocks with β<0.90.
-
The CBOE Volatility Indexes (VIX & Skew Index)
Until now we have seen several methods for analyzing and measuring the current market volatility. The CBOE Volatility Indexes (^VIX and ^SKEW) can do an additional job, and that job is to forecast future market volatility.
Options Volatility as a Forecasting Tool
Volatility is one of the key pricing factors of an options contract. These are the three main factors when pricing an options contract:
-
Intrinsic Value
-
Time-to-Maturity
-
Volatility
Any volatility modification of the underlying instrument makes an option contract more (or less) valuable, as there is a greater (or smaller) probability that the option may expire in-the-money, at the end of its maturity.
■ The Greater the Options Volatility → the Greater the Option Price
Therefore, other things being equal, a higher option price forecasts greater volatility. Consequently, the price of options can be used as a measure of the implied market volatility
□ The Volatility Index: » www.cboe.com/VIX | □ The Skew Index: » www.cboe.com/Skew
Web Tools
There are a lot of web tools that can be used for measuring volatility:
» https://www.mataf.net/en/forex/tools/volatility
» https://www.myfxbook.com/forex-market/volatility
Volatility Can be Good or Bad News Based on the Instrument you Trade and Your Strategy
Volatility can be good or bad depending on the strategy you implement
For a Forex day trader, high volatility is very crucial in order for the currency pair to produce enough movement on the same day. In this way, the trader can profit from substantial intraday price swings. Remember that day traders do not maintain their positions overnight and therefore trading low-volatility assets probably means that they will just have to pay commissions and spreads without any good results.
For a carry trader or a long-term trader, volatility is bad news. Carry traders are trying to profit from the interest-rate differentials and they are not in the mood of being stopped out due to extreme volatility. Long-term traders, on the other hand, trade based on fundamentals, and high volatility for them is just an additional risk that they are unwilling to take.
Volatility can be good or bad depending on the financial instrument you trade
For example:
(i) If you buy a CFD on Gold by placing a near stop-loss order (30-50 pips), volatility is very bad news. Most probably your position will be lost as the volatile Gold will reach your stop-loss level several times in the same day.
(ii) If you buy the same instrument (Gold) by using an Option Contract, volatility is very good news. This is happening as the higher the volatility of the underlying instrument, the more valuable an option contract. As there is a greater probability that the option may expire in-the-money, at the end of its maturity.
■ The greater the options volatility → the greater the option's value
■ Volatility is very important for deep out-of-the-money options
This case was briefly explained before in the section “The CBOE Volatility Indexes (VIX & Skew Index)”.
Basic Conclusions on Market Volatility
Historically, stock market volatility and financial crisis go hand-in-hand. That is why most investors see volatility synonymous with losing money. This is maybe true when you are trading stocks or indices, but when you are trading Forex or Commodities volatility is sometimes bad and sometimes good.
Volatility is good or bad news based on:
(i) Your strategy, and the timeframe you trade
(ii) The financial instrument you trade (Forex, CFDs, Options)
(iii) The financial classes you trade (currencies, commodities, stocks, indices)
A Forex trader who implements an intraday strategy needs volatility in order to make money. As his positions will be closed overnight, high volatility will allow him to profit from intraday price swings.
On the other hand, a Forex trader who implements a swing support/resistance strategy must avoid volatility. High volatility, in this case, incurs the risk of pushing the price below support or above resistance levels and being stopped out. Carry traders and long-term traders don’t like volatility as well, as they see market volatility as an unnecessary risk in their portfolio.
When breaking volatility in the three Forex sessions: the most volatile session is the European (especially as it ends), and the less volatile session is the Asian. Volatility in Forex peaks during the three Forex overlaps and especially during the London/New York overlap. This is because liquidity peaks as the two markets are opened together and usually when liquidity peaks, volatility peaks as well.
As concerns money management, there is a golden rule. Don’t ever overtrade high-volatile assets. Consider capital leverage as an accelerator of volatile positions. As a general rule:
■ When you trade high volatile assets → use low capital leverage and widen your stop-loss
■ When you trade low volatile assets → use higher capital leverage and cut your losses short
■ Decoding Market Volatility
By George M. Protonotarios, financial analyst, » George at Linkedin
Forex-rebates.com (c)
□
PROMOTIONS:
» Forex Brokers Comparison
» Welcome Bonus
» No-Deposit Bonus
» Free VPS Hosting
LEARNING:
» Forex Trading
» Automated Forex
» Technical Analysis
» Fundamental Analysis
TUTORIALS:
» Market Volatility
» Forex Speculation
» Economic Calendars
» Forex Correlations
» News-Trading
Forex Bonus Promotions


100% LQDFX WELCOME BONUS (UP TO $20,000, WITHDRAWABLE)
The 100% LQDFX cash Bonus applies to all deposits above $250, in all account types, and it is instantly credited. You can even withdraw the bonus upon the completion of volume requirements.
■ BONUS DETAILS:
-1- The maximum cumulative amount that can be earned is 20,000 USD/EUR per trading account.
-2- The 100% Bonus Value is calculated as $5 USD per round turn lot traded and can be withdrawn once the total volume requirement has been reached.
-3- Minimum deposit amount to qualify for the 100% bonus is $250 per deposit
□ START HERE:
$50 FBS NO-DEPOSIT (FREE) BONUS
■ BONUS DETAILS:
-1- Verify your Personal area, confirm your e-mail and phone number
-2- Profit received on the bonus funds is withdrawable after 2 lots are traded, and profit reaches $25 or more
-3- Maximum profit made with the Bonus account is $500
□ START HERE:
► $50 FBS (FREE) NO-DEPOSIT BONUS
100% JUSTFOREX WELCOME BONUS (UP TO $20,000, WITHDRAWABLE)
JustForex offer 90 Forex pairs and 39 cryptocurrency pairs, currently, there is a 100% Welcome Bonus promotion
■ BONUS DETAILS:
-1- JUSTFOREX offer a 100% Welcome Bonus of up to 20,000 USD
-2- The minimum deposit to claim the bonus promotion is $100
-3- You can withdraw the bonus and the profits of the bonus, after meeting volume requirements: < Lots > = < Bonus > / 4
□ START HERE:


Trade Forex and Get Back Trading Rebates Based on Your Trading Volumes...
» ECN/STP Forex Brokers Comparison



Take advantage of Welcome Bonus and Participate Contents, you can Combine them all with our Rebate Plans..



Contact today Forex-Rebates and start Trading Forex like a Pro. Forex-Rebates.com is part of the Qexpert.com Group...
» Terms of Use | Privacy














